PIN AI currently supports only Intel SGX (Software Guard Extension) as the TEE hardware and will soon support Intel TDX and NVIDIA GPU TEE. Click here for more information about SGX.
TEE services
Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) provide secure, isolated compute environments for executing sensitive tasks within the PIN AI network. TEE nodes can be configured by network participants to support various workloads and use cases.Services include
- Hosting data connectors: TEEs host and provide confidential compute for Data Connectors, which securely fetch and process user data while preserving privacy.
- Private LLM inference: TEEs run private LLM inference or other privacy-preserving computations necessary for the PIN Network.
TEE device verification
Verification is fundamental to ensuring a trust-minimized environment for TEEs in the PIN Network. This process involves verifying the hardware integrity of a TEE device (e.g., an Intel SGX device), confirming that the CPU is genuine, and that the certificate chain is valid and issued by a trusted manufacturer.Remote Attestation
Before a TEE executes any programs, the process of remote attestation ensures that the TEE is running an untampered version of the expected code, providing security assurances at a hardware level. Data Connectors record verification details as metadata onchain, enabling transparency and auditability. This process is used when registering TEE devices on the network.TEE task validation
This process ensures that tasks executed by a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) node are properly validated and penalized if they fail. TEE task validation follows these steps:- Proof submission: The TEE node submits proof of its work to PIN Network Validators.
- Validation: Validators check if the submitted proof is valid and the task was completed correctly.
- Accountability: If the task fails validation, the TEE node is penalized by slashing its staked funds.
Validation Workflow
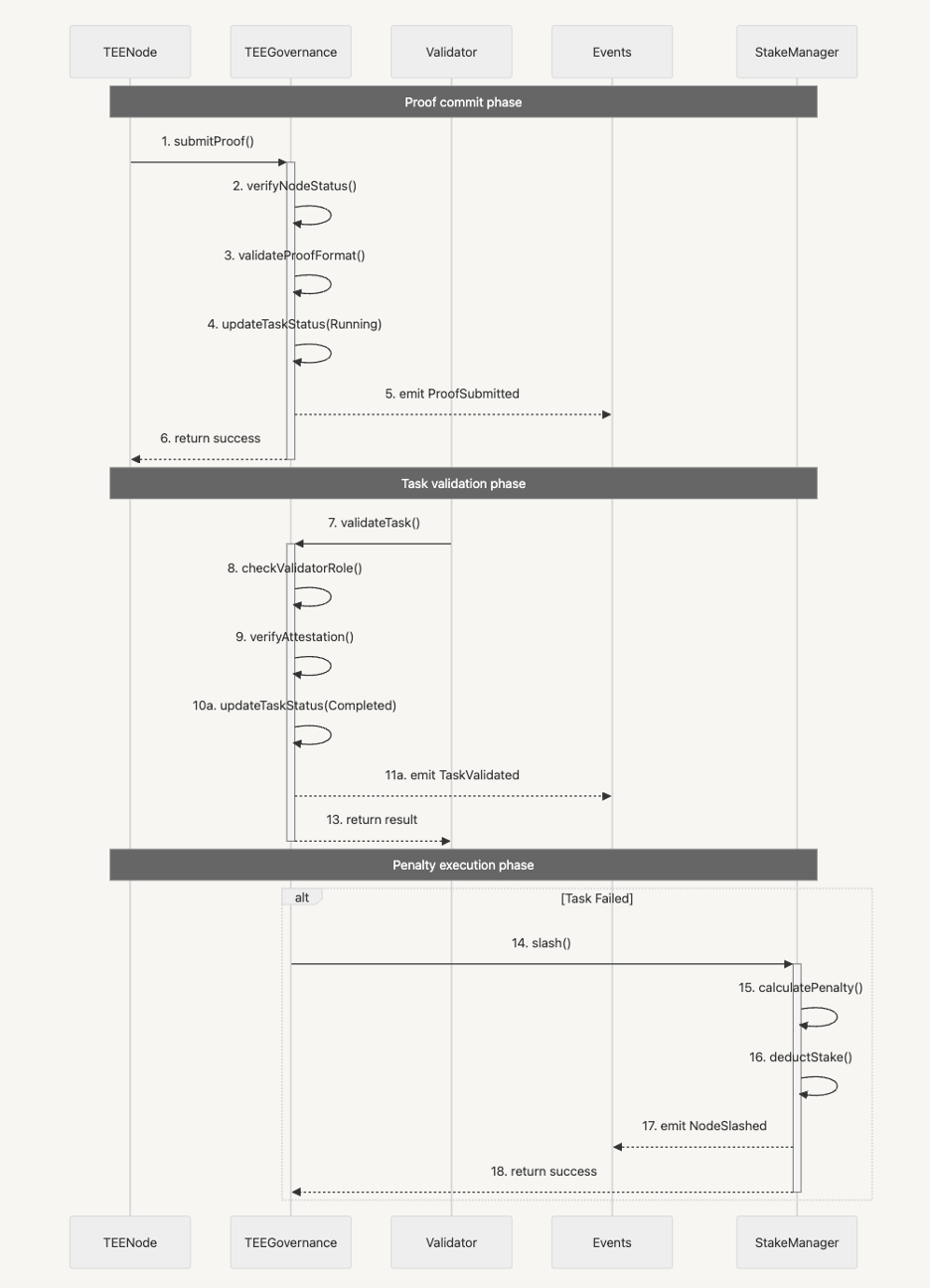
Proof commit phase
The TEE node submits its proof to the TEE Governance contract.- submitProof() (TEE Node → TEE Governance): A TEE node submits proof of task execution to the TEE Governance contract.
- verifyNodeStatus(): TEE Governance verifies the node’s status to ensure it is eligible for task execution.
- validateProofFormat(): TEE Governance validates the format of the proof submitted.
- updateTaskStatus(Running): TEE Governance updates the task status to “Running.”
- emit ProofSubmitted: TEE Governance emits an event indicating that the proof has been submitted.
- Return Success: The process for proof submission is completed successfully.
Task validation phase
The TEE Governance contract triggers the validation process.- validateTask() (TEE Governance → Validator): The TEE Governance contract calls the validator to validate the task.
- checkValidatorRole(): Validator verifies that the caller has the appropriate role to validate the task.
- verifyAttestation(): Validator checks the attestation linked to the task for authenticity and correctness.
- updateTaskStatus(Completed): If the task validation is successful, the Validator updates the task status to “Completed.”
- emit TaskValidated: The Validator emits an event indicating that the task has been validated successfully.
- Return Result: The result of the task validation is returned.
Penalty execution phase
This phase is triggered if task validation fails.- Task Failed (Conditional Execution): If the task validation fails, the penalty execution phase is triggered.
- slash() (TEE Governance → Stake Manager): TEE Governance invokes the slash() function to penalize the node.
- calculatePenalty(): Stake Manager calculates the penalty amount to be deducted.
- deductStake(): Stake Manager deducts the penalty amount from the node’s staked funds.
- emit NodeSlashed: An event is emitted indicating that the node has been slashed.
- Return Success: The penalty execution phase concludes successfully.